Given Australia’s gigantic scale and wild nature, archaeological research can be difficult and costly. Where to start digging on such a vast continent, where the archaeological sites can often be remote and difficult to reach?
Now a joint team of scientists from The University of Sydney, Southern Cross University, Flinders University, and Université Grenoble-Alpes has used new technology to simplify matters. The group recently published its research in the journal Nature Communications.
Australia’s Atlantis
They studied, in particular, the terrain inhabited by the first hunter-gatherers as they traversed Sahul. This is the so-called Australian Atlantis — a supercontinent that existed up to 75,000 years ago and contained Australia, Papua New Guinea, and Tasmania.
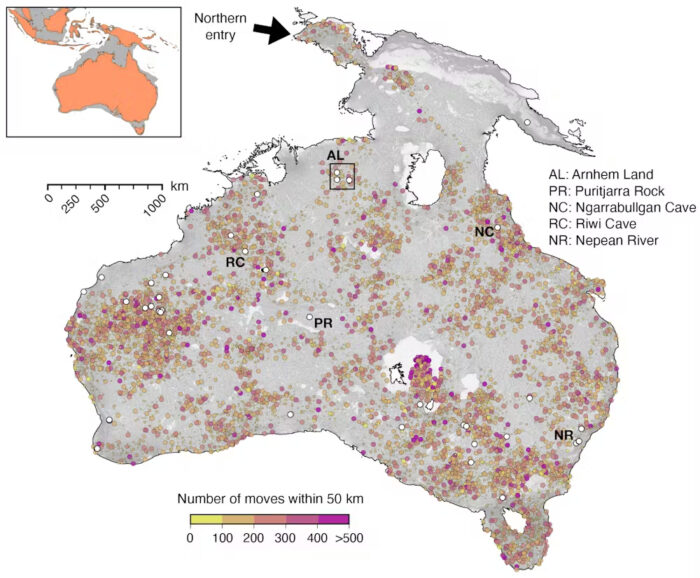
A map of Sahul, the supercontinent that included Australia, Papua New Guinea, and Tasmania. Illustration: Salles et al/Nature Communications
As sea levels rose at the end of the Pleistocene, the landscape took the form we now know. How the first humans reached Sahul is still a mystery, and the paths they took to spread across it are also lost to the sands of time.
A useful tool
Until now. In an article published in The Conversation, the scientists explain their approach. They first chose two likely entry points, “a northern route through West Papua (entry time: 73,000 years ago) and a southern one from the Timor Sea shelf (entry time: about 75,000 years ago).”
A computer model then combined geological evidence of how Sahul changed over time with how hunter-gatherer populations typically spread. The resulting maps show “radiating waves” of migration, with humans following receding coastlines, ancient waterways, and other likely routes since erased by the march of time.
The model also suggests that early humans spread between 0.36 and 1.15 kilometers per year.
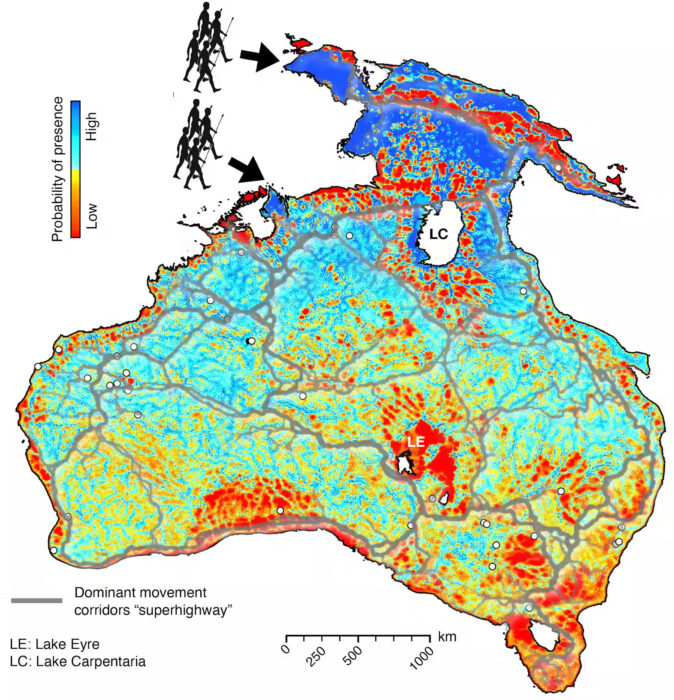
An illustration showing the likely movement patterns of early humans across Sahul. Illustration: Salles et al., Nature Communications
The upshot is a series of maps that will help archaeologists narrow their search for dig sights. The team also hopes their methodology can illuminate other migration mysteries, like the movement of early humans around — and out of — Africa.






